TDM ICIS Workbook 5.5.1.5
From ICISWiki
ICISworkbook Toolbars Set
With the upsurge of ICISworkbook functionalities across the different ICIS Modules, the once single ICISworkbook Toolbar has been divided into four, namely, the ICISwbk-DMS Toolbar, the ICISwbk-GMS Toolbar, the ICISwbk-GEMS Toolbar, and the ICISwbk-SMTA Toolbar. A new INI key "Mode=Full" must be placed in the [Workbook] section of the INI file to view the ICISwbk-GMS Toolbar as this is entirely a new set of functionalities accessing the GMS module. If this INI key is set to "Mode=Advanced", the old hierarchical ICISworkbook Menu, which is intended for new ICIS users, will be hidden as users have become more accustomed in using the toolbar.
The ICISworkbook Toolbars Set
Pedigree Parser
The Pedigree Parser is one of the functionalities accessible through the ICISwbk-GMS Toolbar. It is a pedigree entry tool to the GMS database, continuing the role once faithfully served by the GMS Input application.
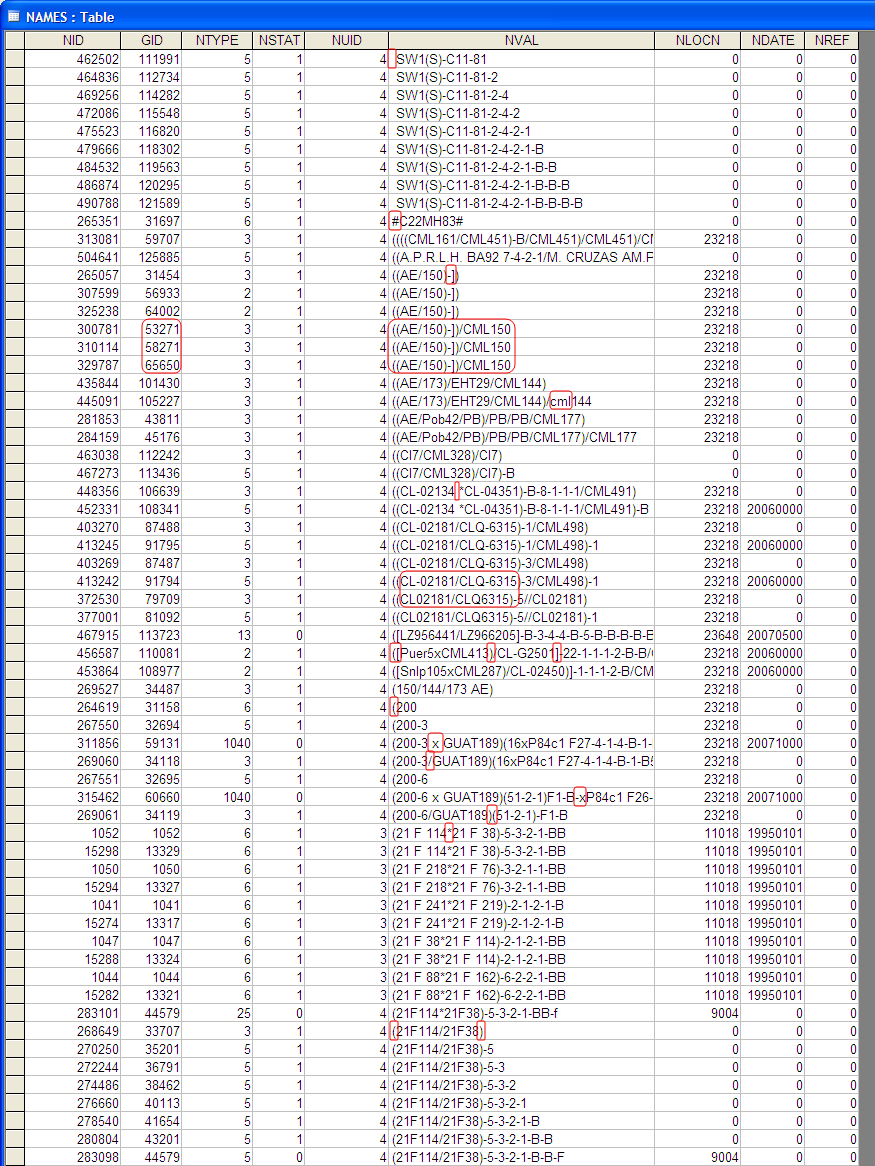
Case Study: Duplicate entries due to lack of an automated name standardization tool
The image below shows a set of unmanaged pedigree strings coming from different breeders having different styles of naming germplasms. The human eye can easily spot slightly varying germplasm names that point to a single germplasm. But for a computer, a single character change implies a totally new entity. Thus, it requires some sort of standardization during data entry of the pedigree string to correctly match varying names and give them a single GID while at the same time maintaining a history of the original string to retain the connection to published works or other data sources.
Errors in an Unmanaged Pedigree Data Storage
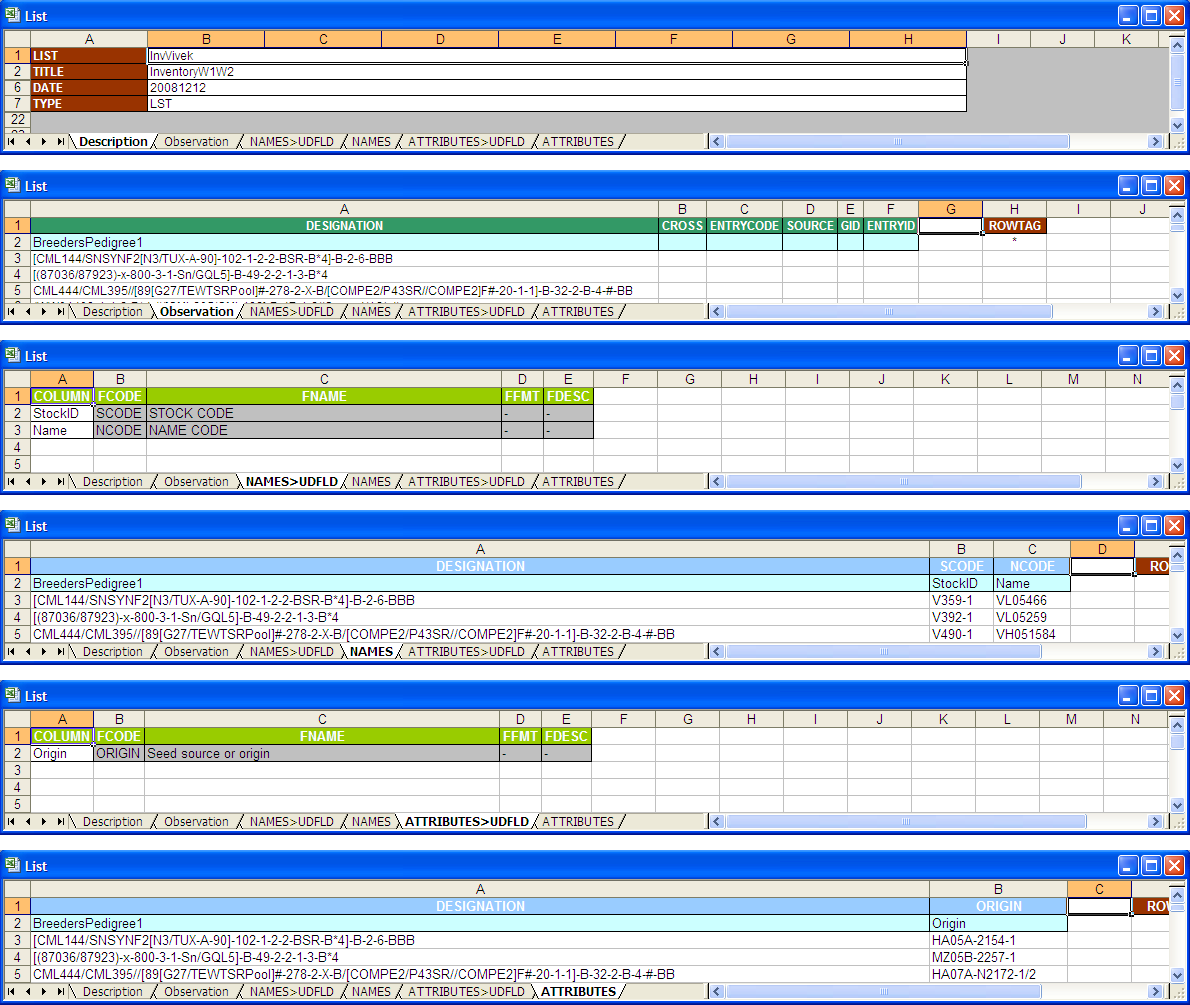
List Template
The List Template
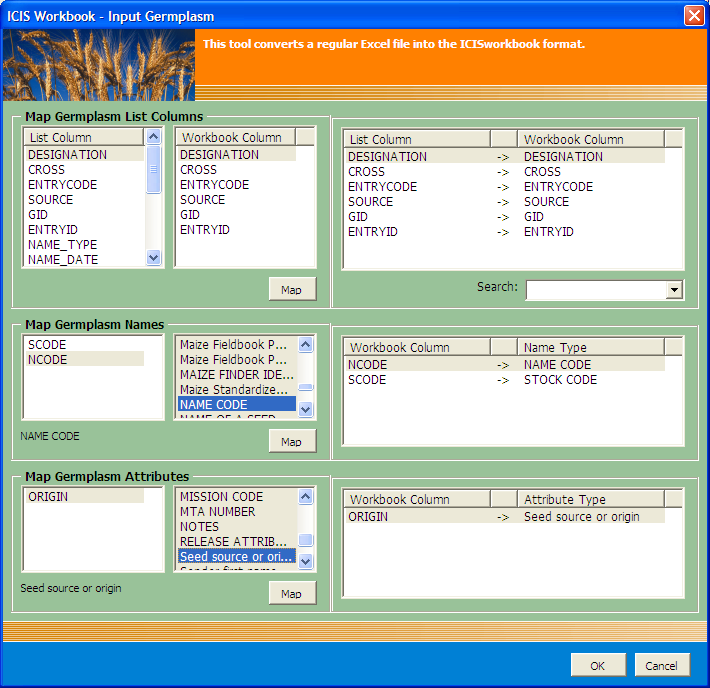
Workbook-to-List Column Mapping Interface
The Workbook-to-List Column Mapping Interface
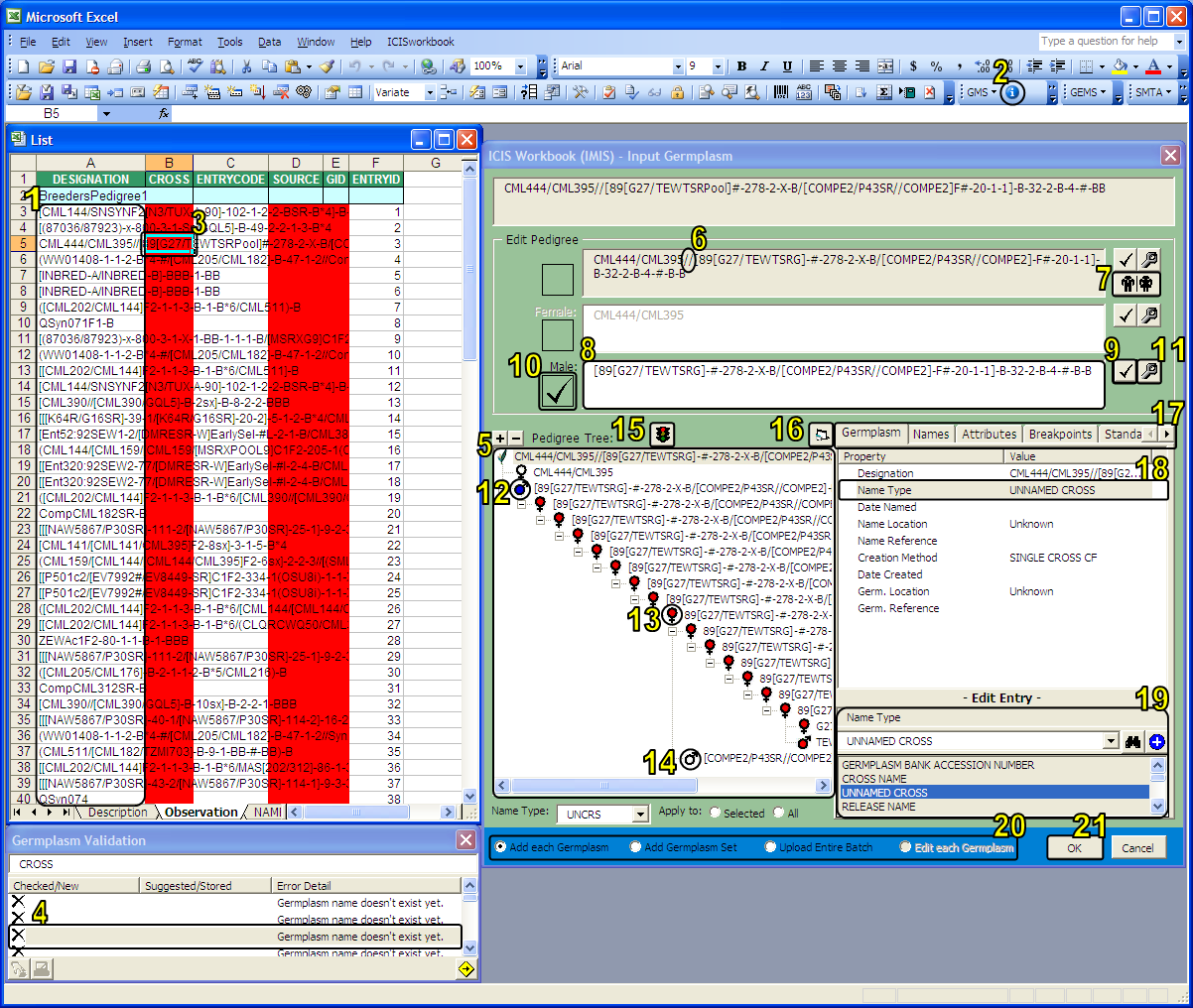
Input Germplasm Interface
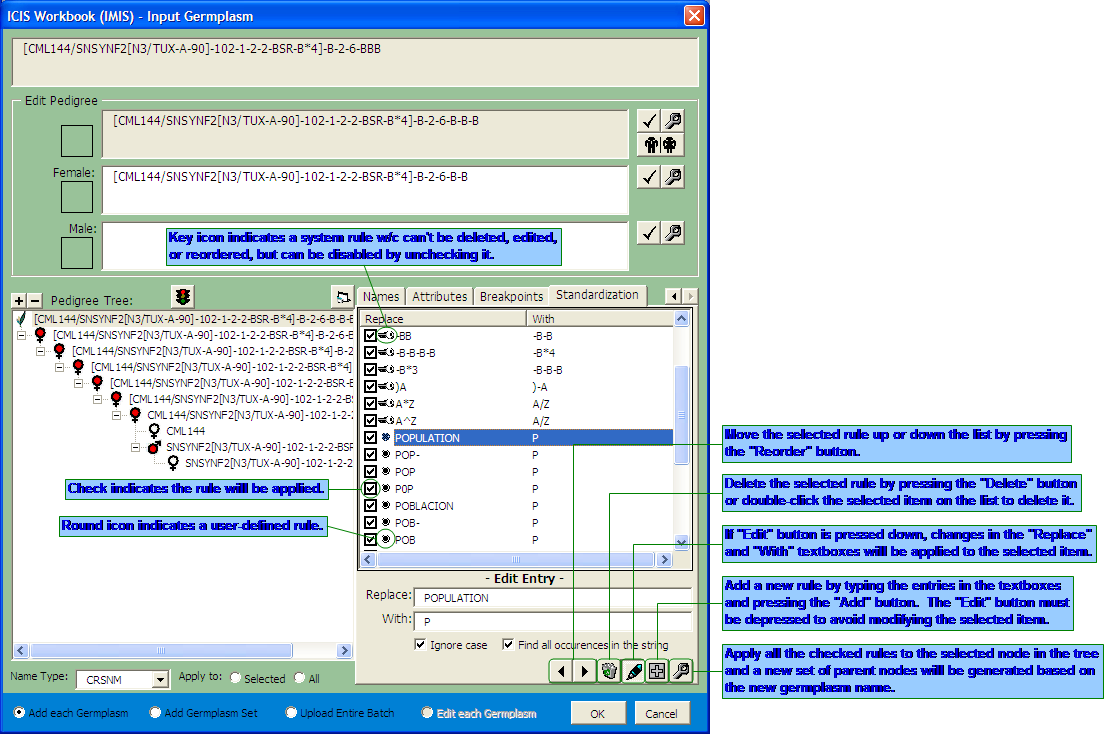
The Input Germplasm Interface of the ICISwbk-GMS Module
1. Start with a list of pedigree strings located under the "Designation" column of a List Template.
2. Click the "Input Germplasm" icon in the ICISwbk-GMS Toolbar to run the function.
3. Not yet existing germplasm names are color-coded with "red" while germplasm names matching multiple GIDs are colored with "orange". Selecting a color-coded cell selects the corresponding error list item in the Germplasm Validation window below.
4. Error details associated with the color-coded cells can be seen in the Germplasm Validation window. Selecting an error list item here would also select the corresponding cell in the worksheet above.
5. The selected germplasm name is automatically broken down into its previous generations and is shown in the form of a pedigree tree.
6. A selected node in the tree can also be manually broken down by placing the mouse cursor anywhere in the string or by highlighting a delimeter character or group of characters in the string.
7. A "Get Parents" button is also available to automatically extract the parents or immediate derivative name from the given string.
8. Extracted parents or source derivative name are placed in editable textboxes so the user can still make corrections in the strings.
9. Manually broken down and/or edited germplasm names can be validated by clicking on the "Check" button.
10. The result of the validity check on the name is displayed as either a "check" or a "question mark" on the side of the name with a higlight on the part of the string that caused the error.
11. Once the error has been resolved, any changes in the germplasm name string can be reflected back to the pedigree tree by clicking on the "Fix" button.
12. Saved changes are indicated by a "blue" node icon. This also means that the germplasm name with this icon has its associated information saved in a temporary file which can be viewed back later. The nodes below the edited node will also change based on the automated parsing of the new string.
13. A "red" node icon indicates a generated name resulting from the automated parsing. This means that any information shown on the tabbed window at the right are all system suggested and are not yet saved.
14. A "white" node icon indicates a germplasm name that already exists in the GMS database. Automated parsing stops when an existing name is encountered, or if it encounters a breakpoint node, or when there are no more recognizable delimeter characters left.
15. A not yet existing germplasm name can be set as a "breakpoint" node by clicking on the "Stop" button such that automated parsing stops there. This is applicable for historical names with one or more characters considered by the system as delimeters but that should no longer be parsed further because it's already the root germplasm.
16. A "Maximize" button is available for viewing large pedigree trees.
17. A tabbed window shows the associated information that goes with the selected germplasm. The contents of the first three tabs, namely, Germplasm, Names, and Attributes change according to the selected node in the pedigree tree. The contents of the last two tabs, namely, Breakpoints and Standardization are not associated with the current germplasm but are used by the system for dedicated functionalities.
Creating your Customized Set of Name Standardization Rules
The Name Standardization Tab of the Input Germplasm Interface
Recorded Rules in the INI File
Extended File Conversion Wizard
Case Study: From Maize Fieldbook file format (or any other Excel file) to ICISworkbook file format in one click
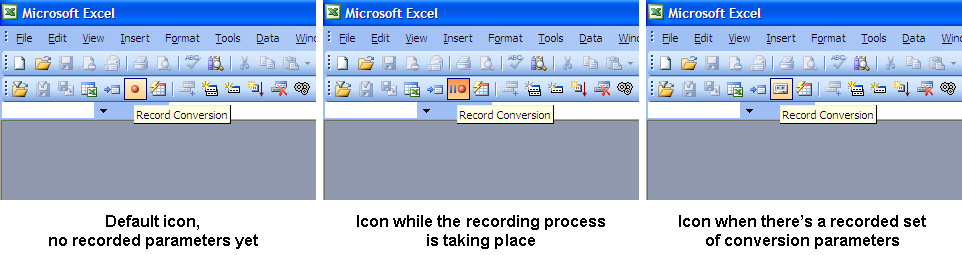
Record Conversion Button
The Record Conversion Button